HTML5
一、什么是 HTML5
HTML5的概念与定义- 定义:
HTML5定义了HTML标准的最新版本,是对HTML的第五次重大修改,号称下一代的HTML - 两个概念:
- 是一个新版本的
HTML语言,定义了新的标签、特性和属性 - 拥有一个强大的技术集,这些技术集是指:
HTML5、CSS3、javascript, 这也是广义上的HTML5
- 定义:
HTML5拓展了哪些内容- 语义化标签
- 本地存储
- 兼容特性
2D、3D- 动画、过渡
CSS3特性- 性能与集成
HTML5的现状绝对多数新的属性,都已经被浏览器所支持,最新版本的浏览器已经开始陆续支持最新的特性,
总的来说:
HTML5已经是大势所趋
二、HTML5 新增标签
- 什么是语义化
新增了那些语义化标签
- `header` --- 头部标签 - `nav` --- 导航标签 - `article` --- 内容标签 - `section` --- 块级标签 - `aside` --- 侧边栏标签 - `footer` --- 尾部标签
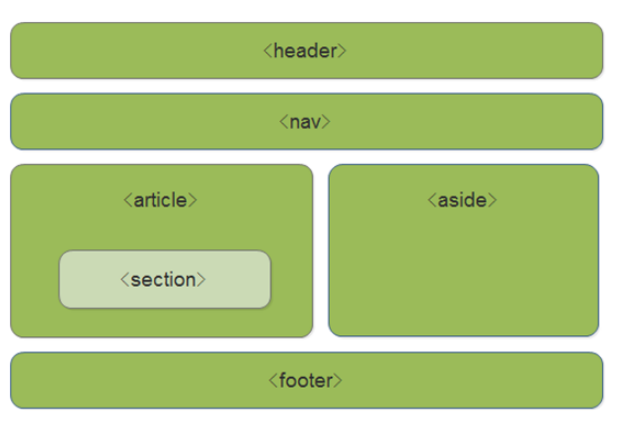
使用语义化标签的注意
- 语义化标签主要针对搜索引擎 - 新标签可以使用一次或者多次 - 在 `IE9` 浏览器中,需要把语义化标签都转换为块级元素 - 语义化标签,在移动端支持比较友好, - 另外,`HTML5` 新增的了很多的语义化标签,随着课程深入,还会学习到其他的
三、多媒体音频标签
多媒体标签有两个,分别是
- 音频 --
audio - 视频 --
video
- 音频 --
audio标签说明- 可以在不使用标签的情况下,也能够原生的支持音频格式文件的播放,
- 但是:播放格式是有限的
audio 支持的音频格式
- audio 目前支持三种格式

- audio 的参数
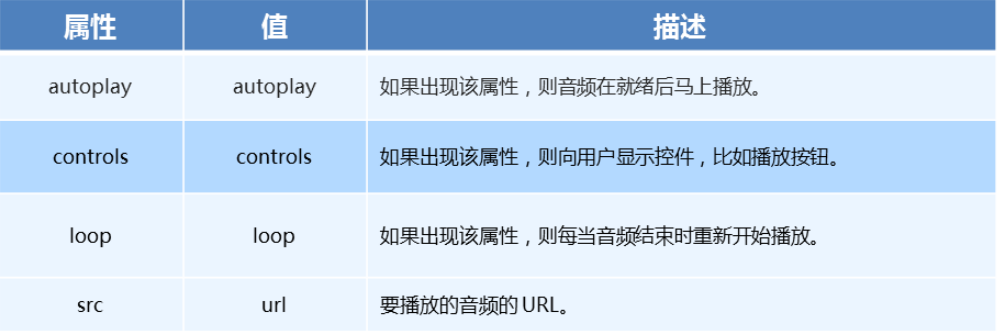
5、audio 代码演示
<body>
<!-- 注意:在 chrome 浏览器中已经禁用了 autoplay 属性 -->
<!-- <audio src="./media/snow.mp3" controls autoplay></audio> -->
<!--
因为不同浏览器支持不同的格式,所以我们采取的方案是这个音频准备多个文件
-->
<audio controls>
<source src="./media/snow.mp3" type="audio/mpeg" />
</audio>
</body>四、多媒体视频标签
video 视频标签
- 目前支持三种格式
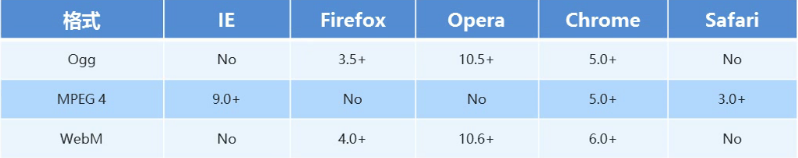
语法格式
<video src="./media/video.mp4" controls="controls"></video>- video 参数
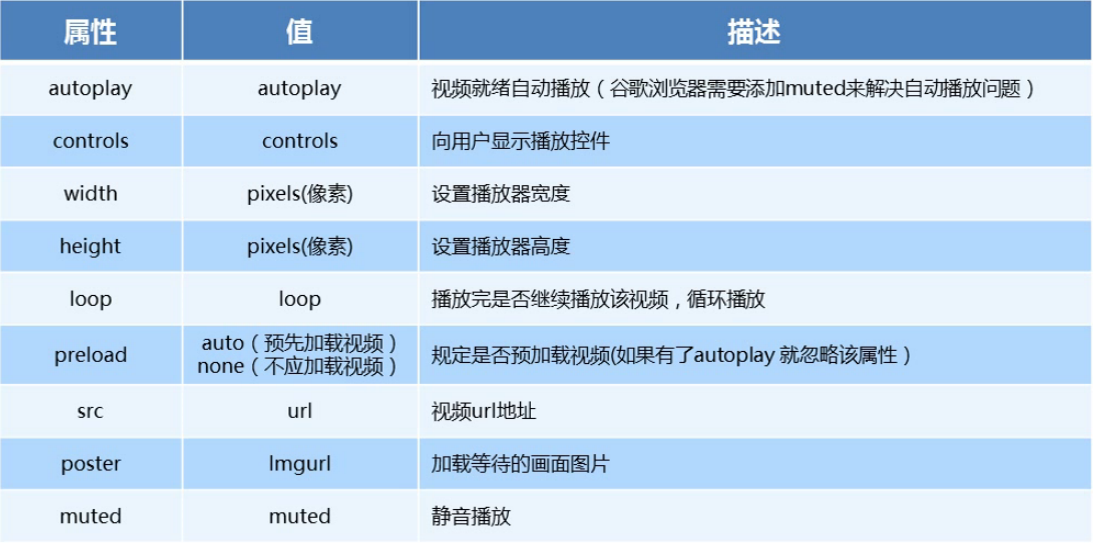
video 代码演示
<body> <!-- <video src="./media/video.mp4" controls="controls"></video> --> <!-- 谷歌浏览器禁用了自动播放功能,如果想自动播放,需要添加 muted 属性 --> <video controls="controls" autoplay muted loop poster="./media/pig.jpg"> <source src="./media/video.mp4" type="video/mp4"> <source src="./media/video.ogg" type="video/ogg"> </video> </body>多媒体标签总结
- 音频标签与视频标签使用基本一致
- 多媒体标签在不同浏览器下情况不同,存在兼容性问题
- 谷歌浏览器把音频和视频标签的自动播放都禁止了
- 谷歌浏览器中视频添加 muted 标签可以自己播放
- 注意:重点记住使用方法以及自动播放即可,其他属性可以在使用时查找对应的手册
五、新增 input 标签
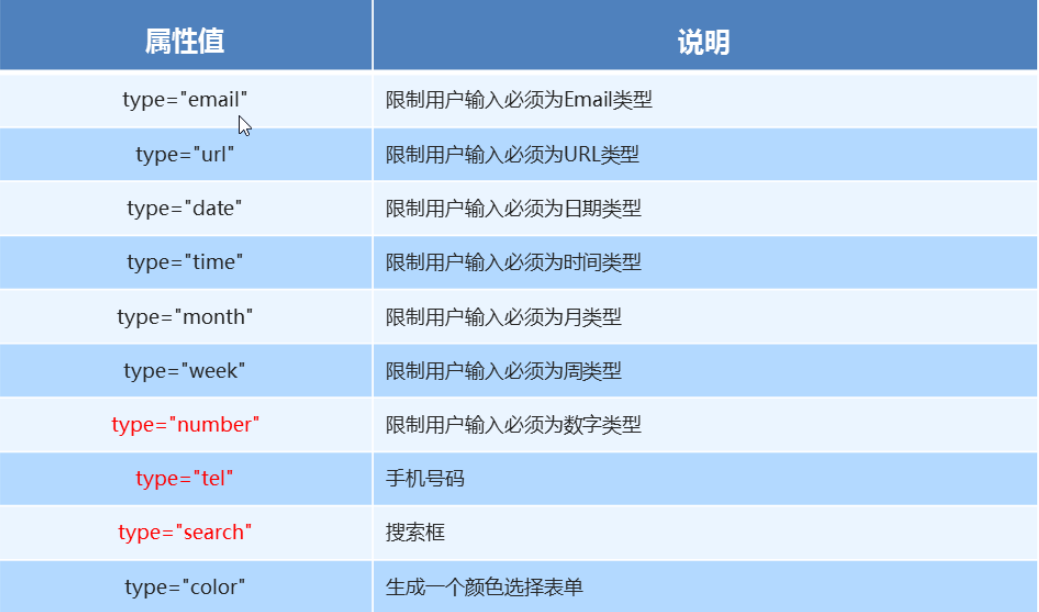
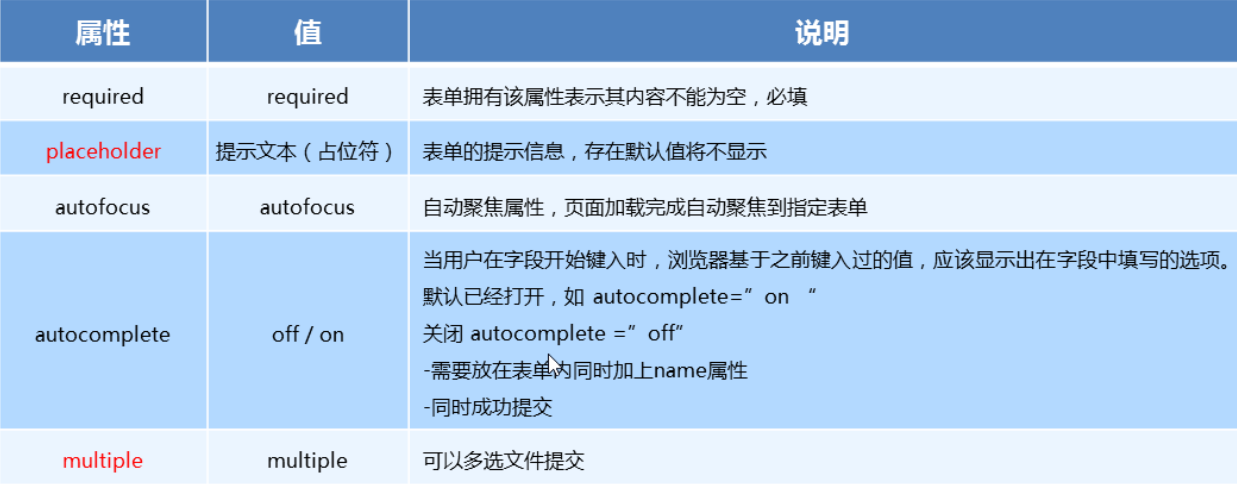
六、新增表单属性
七、CSS3 属性选择器(上)
什么是
CSS3- 在
CSS2的基础上拓展、新增的样式
- 在
CSS3发展现状- 移动端支持优于
PC端 CSS3目前还草案,在不断改进中CSS3相对H5,应用非常广泛
- 移动端支持优于
- 属性选择器列表
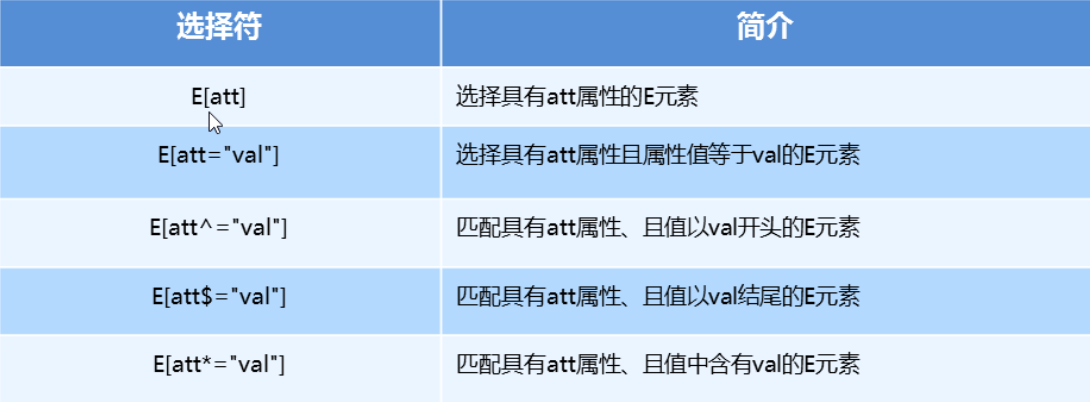
属性选择器代码演示
button { cursor: pointer; } button[disabled] { cursor: default }
八、CSS3 属性选择器(下)
代码演示
input[type=search] { color: skyblue; } span[class^=black] { color: lightgreen; } span[class$=black] { color: lightsalmon; } span[class*=black] { color: lightseagreen; }
九、结构伪类选择器
- 属性列表
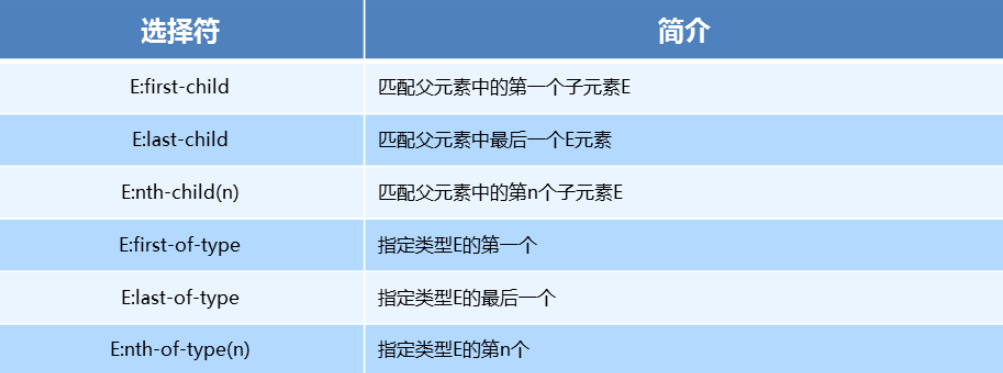
代码演示
ul li:first-child { background-color: lightseagreen; } ul li:last-child { background-color: lightcoral; } ul li:nth-child(3) { background-color: aqua; }
十、nth-child 参数详解
nth-child 详解
- 注意:本质上就是选中第几个子元素
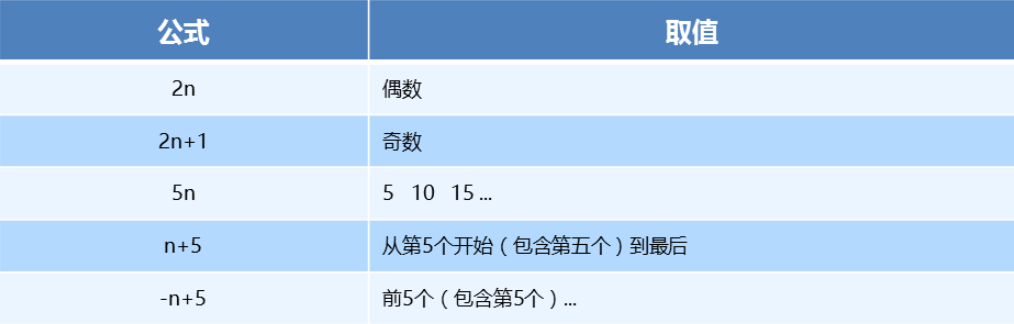
- n 可以是数字、关键字、公式
- n 如果是数字,就是选中第几个
- 常见的关键字有
even偶数、odd奇数 - 常见的公式如下(如果 n 是公式,则从 0 开始计算)
- 但是第 0 个元素或者超出了元素的个数会被忽略
代码演示
<style> /* 偶数 */ ul li:nth-child(even) { background-color: aquamarine; } /* 奇数 */ ul li:nth-child(odd) { background-color: blueviolet; } /*n 是公式,从 0 开始计算 */ ul li:nth-child(n) { background-color: lightcoral; } /* 偶数 */ ul li:nth-child(2n) { background-color: lightskyblue; } /* 奇数 */ ul li:nth-child(2n + 1) { background-color: lightsalmon; } /* 选择第 0 5 10 15, 应该怎么选 */ ul li:nth-child(5n) { background-color: orangered; } /* n + 5 就是从第5个开始往后选择 */ ul li:nth-child(n + 5) { background-color: peru; } /* -n + 5 前五个 */ ul li:nth-child(-n + 5) { background-color: tan; } </style>
十一、nth-child 和 nt-of-type 的区别
代码演示
<style> div :nth-child(1) { background-color: lightblue; } div :nth-child(2) { background-color: lightpink; } div span:nth-of-type(2) { background-color: lightseagreen; } div span:nth-of-type(3) { background-color: #fff; } </style>区别
nth-child选择父元素里面的第几个子元素,不管是第几个类型nt-of-type选择指定类型的元素
十二、伪元素选择器
- 伪类选择器

伪类选择器注意事项
before和after必须有content属性before在内容前面,after 在内容后面before和after创建的是一个元素,但是属于行内元素- 创建出来的元素在
Dom中查找不到,所以称为伪元素 - 伪元素和标签选择器一样,权重为 1
代码演示
<style> div { width: 100px; height: 100px; border: 1px solid lightcoral; } div::after, div::before { width: 20px; height: 50px; text-align: center; display: inline-block; } div::after { content: '德'; background-color: lightskyblue; } div::before { content: '道'; background-color: mediumaquamarine; } </style>
十三、伪元素的案例
添加字体图标
p { width: 220px; height: 22px; border: 1px solid lightseagreen; margin: 60px; position: relative; } p::after { content: '\ea50'; font-family: 'icomoon'; position: absolute; top: -1px; right: 10px; }
十四、2D 转换之 translate
2D转换2D转换是改变标签在二维平面上的位置和形状- 移动:
translate - 旋转:
rotate - 缩放:
scale
translate语法- x 就是 x 轴上水平移动
- y 就是 y 轴上水平移动
transform: translate(x, y) transform: translateX(n) transfrom: translateY(n)重点知识点
2D的移动主要是指 水平、垂直方向上的移动translate最大的优点就是不影响其他元素的位置translate中的100%单位,是相对于本身的宽度和高度来进行计算的- 行内标签没有效果
- 代码演示
div {
background-color: lightseagreen;
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
/* 平移 */
/* 水平垂直移动 100px */
/* transform: translate(100px, 100px); */
/* 水平移动 100px */
/* transform: translate(100px, 0) */
/* 垂直移动 100px */
/* transform: translate(0, 100px) */
/* 水平移动 100px */
/* transform: translateX(100px); */
/* 垂直移动 100px */
transform: translateY(100px)
}十五、让一个盒子水平垂直居中
看代码
<style> div { position: relative; width: 500px; height: 500px; background-color: blue; /* 1. 我们tranlate里面的参数是可以用 % */ /* 2. 如果里面的参数是 % 移动的距离是 盒子自身的宽度或者高度来对比的 */ /* 这里的 50% 就是 50px 因为盒子的宽度是 100px */ /* transform: translateX(50%); */ } p { position: absolute; top: 50%; left: 50%; width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: purple; /* margin-top: -100px; margin-left: -100px; */ /* translate(-50%, -50%) 盒子往上走自己高度的一半 */ transform: translate(-50%, -50%); } span { /* translate 对于行内元素是无效的 */ transform: translate(300px, 300px); } </style> <body> <div> <p></p> </div> <span>123</span> </body>十六、
2D 转换 rotate
rotate 旋转
2D旋转指的是让元素在二维平面内顺时针或者逆时针旋转
rotate语法/* 单位是:deg */ transform: rotate(度数)重点知识点
rotate里面跟度数,单位是deg- 角度为正时,顺时针,角度为负时,逆时针
- 默认旋转的中心点是元素的中心点
代码演示
img:hover { transform: rotate(360deg) }一、rotate
2d旋转指的是让元素在2维平面内顺时针旋转或者逆时针旋转
使用步骤:
- 给元素添加转换属性
transform - 属性值为
rotate(角度)如transform:rotate(30deg)顺时针方向旋转30度
div{
transform: rotate(0deg);
}二、三角
- 代码演示
二、设置元素旋转中心点(transform-origin)
transform-origin基础语法transform-origin: x y;重要知识点
- 注意后面的参数 x 和 y 用空格隔开
- x y 默认旋转的中心点是元素的中心 (50% 50%),等价于
centercenter - 还可以给 x y 设置像素或者方位名词(
top、bottom、left、right、center)
三、旋转中心案例
- 代码演示
四、2D 转换之 scale
scale的作用- 用来控制元素的放大与缩小
语法
transform: scale(x, y)知识要点
- 注意,x 与 y 之间使用逗号进行分隔
transform: scale(1, 1): 宽高都放大一倍,相当于没有放大transform: scale(2, 2): 宽和高都放大了二倍transform: scale(2): 如果只写了一个参数,第二个参数就和第一个参数一致transform:scale(0.5, 0.5): 缩小scale最大的优势:可以设置转换中心点缩放,默认以中心点缩放,而且不影响其他盒子
代码演示
div:hover { /* 注意,数字是倍数的含义,所以不需要加单位 */ /* transform: scale(2, 2) */ /* 实现等比缩放,同时修改宽与高 */ /* transform: scale(2) */ /* 小于 1 就等于缩放*/ transform: scale(0.5, 0.5) }
五、图片放大案例
- 代码演示
六、分页按钮案例
- 代码演示
七、 2D 转换综合写法以及顺序问题
知识要点
- 同时使用多个转换,其格式为
transform: translate() rotate() scale() - 顺序会影响到转换的效果(先旋转会改变坐标轴方向)
- 但我们同时有位置或者其他属性的时候,要将位移放到最前面
- 同时使用多个转换,其格式为
代码演示
div:hover { transform: translate(200px, 0) rotate(360deg) scale(1.2) }
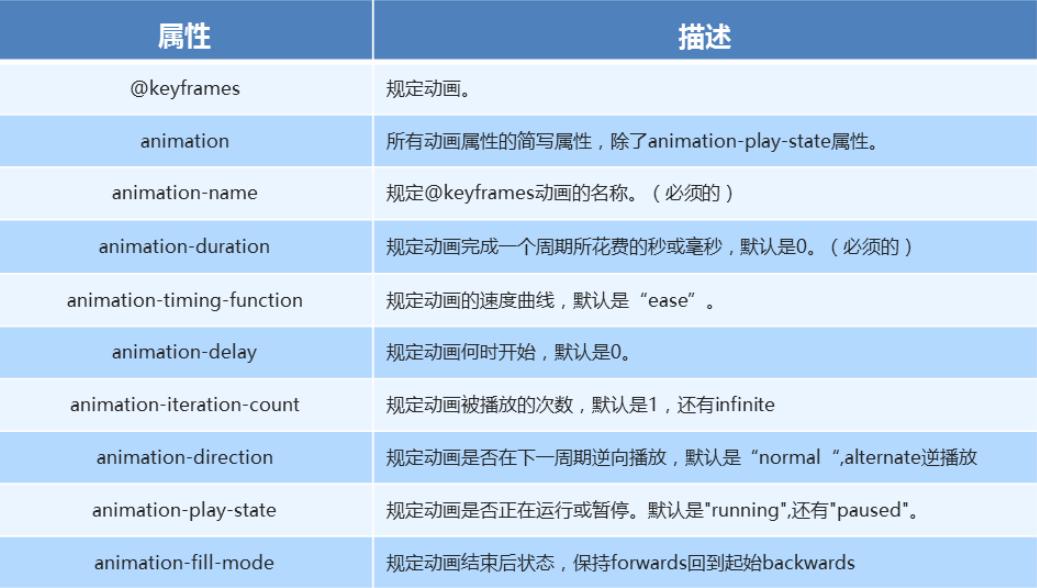
八、 动画(animation)
什么是动画
- 动画是
CSS3中最具颠覆性的特征之一,可通过设置多个节点来精确的控制一个或者一组动画,从而实现复杂的动画效果
- 动画是
动画的基本使用
- 先定义动画
- 在调用定义好的动画
语法格式(定义动画)
@keyframes 动画名称 { 0% { width: 100px; } 100% { width: 200px } }- 语法格式(使用动画)
div {
/* 调用动画 */
animation-name: 动画名称;
/* 持续时间 */
animation-duration: 持续时间;
}动画序列
- 0% 是动画的开始,100 % 是动画的完成,这样的规则就是动画序列
- 在 @keyframs 中规定某项 CSS 样式,就由创建当前样式逐渐改为新样式的动画效果
- 动画是使元素从一个样式逐渐变化为另一个样式的效果,可以改变任意多的样式任意多的次数
- 用百分比来规定变化发生的时间,或用
from和to,等同于 0% 和 100%
代码演示
<style> div { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: aquamarine; animation-name: move; animation-duration: 0.5s; } @keyframes move{ 0% { transform: translate(0px) } 100% { transform: translate(500px, 0) } } </style>
九、动画序列
- 代码演示
十、动画常见属性
- 常见的属性
代码演示
div { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: aquamarine; /* 动画名称 */ animation-name: move; /* 动画花费时长 */ animation-duration: 2s; /* 动画速度曲线 */ animation-timing-function: ease-in-out; /* 动画等待多长时间执行 */ animation-delay: 2s; /* 规定动画播放次数 infinite: 无限循环 */ animation-iteration-count: infinite; /* 是否逆行播放 */ animation-direction: alternate; /* 动画结束之后的状态 */ animation-fill-mode: forwards; } div:hover { /* 规定动画是否暂停或者播放 */ animation-play-state: paused; }
十一、 动画简写方式
动画简写方式
/* animation: 动画名称 持续时间 运动曲线 何时开始 播放次数 是否反方向 起始与结束状态 */ animation: name duration timing-function delay iteration-count direction fill-mode知识要点
- 简写属性里面不包含
animation-paly-state - 暂停动画
animation-paly-state: paused; 经常和鼠标经过等其他配合使用 - 要想动画走回来,而不是直接调回来:
animation-direction: alternate - 盒子动画结束后,停在结束位置:
animation-fill-mode: forwards
- 简写属性里面不包含
代码演示
animation: move 2s linear 1s infinite alternate forwards;
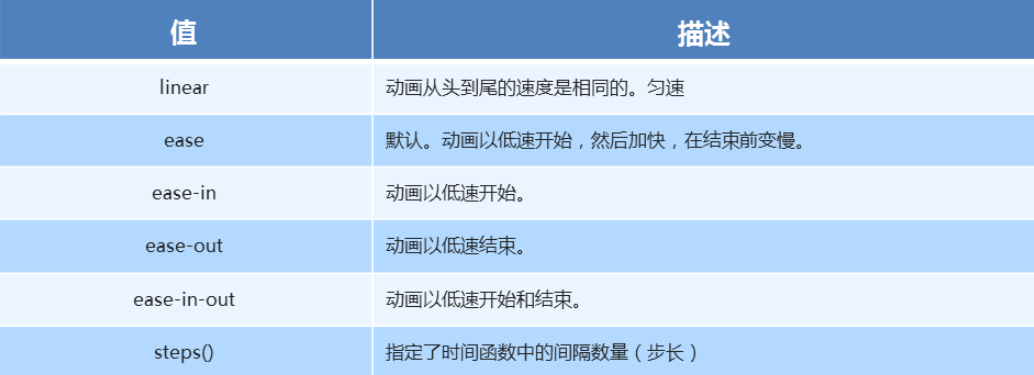
十二、速度曲线细节
速度曲线细节
animation-timing-function: 规定动画的速度曲线,默认是ease
代码演示
div { width: 0px; height: 50px; line-height: 50px; white-space: nowrap; overflow: hidden; background-color: aquamarine; animation: move 4s steps(24) forwards; } @keyframes move { 0% { width: 0px; } 100% { width: 480px; } }
十三、奔跑的熊大
- 代码演示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
body {
background-color: #ccc;
}
div {
position: absolute;
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background: url(media/bear.png) no-repeat;
/* 我们元素可以添加多个动画, 用逗号分隔 */
animation: bear .4s steps(8) infinite, move 3s forwards;
}
@keyframes bear {
0% {
background-position: 0 0;
}
100% {
background-position: -1600px 0;
}
}
@keyframes move {
0% {
left: 0;
}
100% {
left: 50%;
/* margin-left: -100px; */
transform: translateX(-50%);
}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
评论 (0)